public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(plus(3, 4));
}
public static int plus(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
public static int plus02(int a, int b, int c) {
return a+b+c;
}
public static double plus03(double a, double b) {
return a+b;
}
public static double plus0302(double a, double b, double c) {
return a+b+c;
}
}이런 코드를
package class02;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(plus(3, 4));
}
public static int plus(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
public static int plus(int a, int b, int c) {
return a+b+c;
}
public static double plus(double a, double b) {
return a+b;
}
public static double plus(double a, double b, double c) {
return a+b+c;
}
}이렇게 함수명을 plus로 통일
함수명 중복 정의를 허용 하는 것 -> 오버로딩!!
기능이 같은데 메서드 시그니처가 다른 경우에 허용한다
기능이 다르면 XX
객체지향 프로그래밍 OOP

클래스
자료형을 코딩한다고 하자
대문자로 시작
new 연산자를 통해서만 객체를 얻을 수 있다
인스턴스(객체) : new를 통해 나온 객체

갈색 글씨 num은 변수이고
파란 글씨 c1은 멤버변수이다

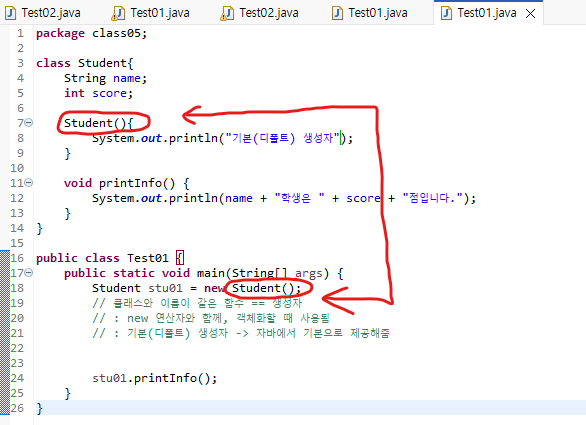
왼쪽 Student : 자료형
오른쪽 Student : 함수
클래스와 이름이 같은 함수 == 생성자
: new 연산자와 함께, 객체화할 때 사용됨

멤버 변수 초기화는 생성자를 통해서 가능하다
stu02
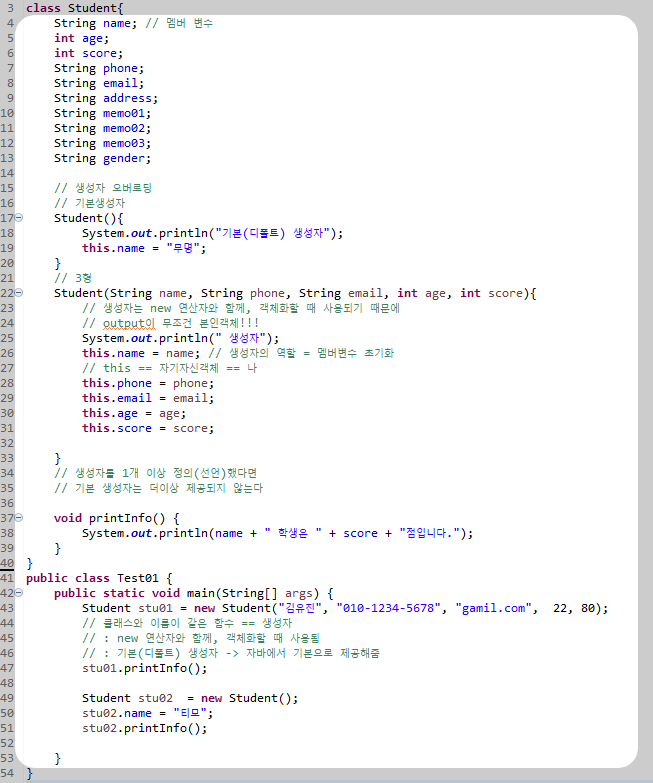
<생성자>
클래스와 이름이 같은 함수
객체화할 때 사용
멤버 변수 초기화
>> 기본생성자는 제공 XX
>> 선언하면 됨 -> 생성자 오버로딩
<this>
자기자신객체
'🍏 개발일기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 학생부 프로그램 (0) | 2025.10.15 |
|---|---|
| 매개변수(parameter)와 인수(argument)의 차이 (0) | 2025.10.14 |
| 함수 (0) | 2025.10.13 |
| 이진 탐색 (0) | 2025.09.26 |
| 최소값 찾기 : 디버깅표 그리기 (0) | 2025.09.24 |